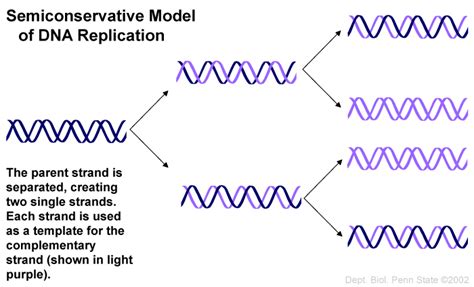
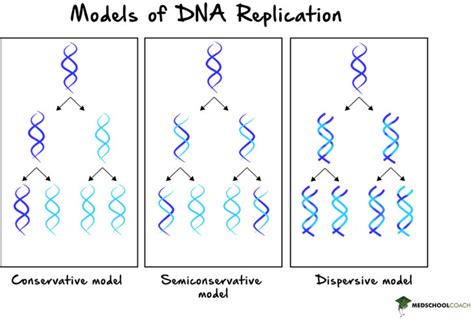
conservative semiconservative and dispersive replication There were three models suggested for DNA replication: conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive. The conservative method of replication suggests that parental DNA remains together and newly-formed daughter strands are also together. Coated canvas can easily be cleaned with a damp cloth and slightly soapy water. Home remedies such as mink oil, perfume, lcohol-based solutions such as hand sanitizers, leather lotions, cleaners, or chemicals, should not be used on any canvas products. The use of such remedies may cause the canvas to wear adversely and prematurely.
0 · why is dna replication semi conservative
1 · what is semi conservative dna replication
2 · steps of semi conservative replication
3 · semiconservative replication vs conservative
4 · semiconservative replication template
5 · semiconservative replication model
6 · how was semiconservative replication proved
7 · dna replication is said to be semiconservative which of the fol
You will need approximately the following quantities of fish to level from 1-300 Cooking: 50 Raw Brilliant Smallfish; 50 Raw Longjaw Mud Snapper; 75 Raw Bristle Whisker Catfish; 50 Raw Mithril Head Trout; 25 Raw Spotted Yellowtail; 25 Raw Sunscale Salmon; 25 Large Raw Mightfish; Leveling Cooking As a Rogue
There were three models suggested for DNA replication: conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive. The conservative method of replication suggests that parental DNA remains together and newly-formed daughter strands are also together.
In conservative replication, the original DNA strands stay associated with each other, while the newly made DNA forms its own double-helix. Semi-conservative replication posits the creati. In conservative replication, the original DNA strands stay associated with each other, while the newly made DNA forms its own double-helix. Semi-conservative replication posits the creation of hybrid old-new .Conceptually, semiconservative replication made sense in light of the double helix structural model of DNA, in particular its complementary nature and the fact that adenine always pairs .
Semi-conservative replication. DNA replication has three possible methods: conservative, dispersive, and semi-conservative. Here, we focus on the Meselson-Stahl experiment, which .The Meselson–Stahl experiment is an experiment by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958 which supported Watson and Crick's hypothesis that DNA replication was . The semi-conservative method suggests that each of the two parental DNA strands act as a template for new DNA to be synthesized; after replication, each double .Semi-Conservative, Conservative, & Dispersive models of DNA replication. In the semi-conservative model, the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself. After one round of replication, the two daughter molecules .
Semiconservative replication describes the mechanism of DNA replication in all known cells. DNA replication occurs on multiple origins of replication along the DNA template strands. As . DNA replication initiated from origins of replication proceeds in a semiconservative manner, such that each new copy of double-stranded DNA contains one . Evidence for Semi-Conservative Replication of DNA in Prokaryotes. Using isotopically labeled DNA and an isopycnic density gradient centrifugation technique, M. Meselson, and F.W. Stahl successfully .
ADVERTISEMENTS: Theoretically, there are the following three possible modes of DNA replication: (1) Dispersive, (2) Conservative and ADVERTISEMENTS: (3) Semi-conservative. 1. Dispersive Replication: In dispersive replication, the parent DNA molecule is broken into several pieces, and the ‘new’ molecules will consist of both old and newly synthesized .Semi-Conservative, Conservative, & Dispersive models of DNA replication. In the semi-conservative model, the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself. After one round of replication, the two daughter .The double-helix model suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. What was not clear was how the replication took place. There were three models suggested (): conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive. Semiconservative Replication: This hypothesis was proposed by Watson and Crick on the basis of their model of DNA molecule. They proposed that the DNA molecule untwists and start separating at one end. . This could happen with either semi-conservative or dispersive replication. Thus the possibility of conservative replication was eliminated.
Semi-conservative replication posits the creation of hybrid old-new double helices. Dispersive replication proposed molecules composed of randomized fragments of double-old and double-new DNA. One of the most important concepts of DNA replication is that it is a semi-conservative process (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)). This means that every double .
Two other models, "Conservative" and "Dispersive", for DNA replication were proposed. Setting Up the Experiment. A method was needed to detect a difference between the parental and daughter (newly replicated) DNA strands. Then, one could follow the parent DNA molecule in . Different model of DNA Replication: Three form of DNA replication can be notable: conservative, semiconservative, dispersive. Semi-conservative replication. The two parental strands of DNA unwrap from one another in this concept, and each serve as a template for the synthesis of a new, complimentary strand. This suggested either a semi-conservative or dispersive mode of replication. The DNA harvested from cells grown for two generations in 14 N formed two bands: one DNA band was at the intermediate position between 15 N and 14 N, and the other corresponded to the band of 14 N DNA.
why is dna replication semi conservative
Compare conservative, semiconservative, and dispersive modes of DNA replication In conservative all of the old dna is passed to the offspring with no introduction of new dna. In semiconservative, each daughter strand is made of one old dna strand and one new dna strand.The results after two divisions supported the semi-conservative model of DNA replication. After one division, DNA molecules were found to contain a mix of 15 N and 14 N, disproving the conservative mod el; After two divisions, some molecules of DNA were found to consist solely of 14 N, disproving the dispersive model; Results of the Meselson .
Between 1953 and 1957, before the Meselson-Stahl experiment verified semi-conservative replication of DNA, scientists debated how DNA replicated. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick proposed that DNA was composed of two helical strands that wound together in a coil. Their model suggested a replication mechanism, later termed semi-conservative replication, in .
After one round of replication, the DNA sedimented halfway between the 15 N and 14 N levels (purple band), ruling out the conservative model of replication. After a second round of replication, the dispersive model of replication was ruled out. These data supported the semiconservative replication model.Theoretical modes of DNA replication There are three theoretical modes of DNA replication: semiconservative replication, conservative replication, and dispersive replication. In semiconservative replication, each daughter DNA molecule has one parental DNA strand. In conservative replication, one daughter DNA molecule is made completely of newly .The results of the Meselson-Stahl experiment supported a semiconservative model of DNA replication. The first replication in the 14 N medium produced a band of hybrid (14N and 15N) DNA. This result eliminated the conservative model of replication. The second replication in the 14N medium produced both light (14N) DNA and hybrid (14N and 15N .
The double-helix model suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. What was not clear was how the replication took place. There were three models suggested : conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive.The Meselson–Stahl experiment is an experiment by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958 which supported Watson and Crick's hypothesis that DNA replication was semiconservative.In semiconservative replication, when the double-stranded DNA helix is replicated, each of the two new double-stranded DNA helices consisted of one strand from the .Distinguishing semiconservative replication from nonconservative repair replication by using density labeling with 5BU. As with the excision repair of damage (like cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers), the heteroduplex regions generated during genetic recombination were thought to provoke localized excision of a tract of nucleotides from one strand .
Stent introduced DNA replication classes that, if present in DNA, would yield distinct experimental results. Conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive DNA replication categories shaped scientists' research into how DNA replicated, which led to the conclusion that DNA replicated semi-conservatively.After Watson and Crick proposed the double helix model of DNA, three models for DNA replication were proposed: conservative, semiconservative and dispersive. But Meselson and Stahl proved semiconservative is actual the mode of DNA replication . So, dispersive and conservative replication are just hypothesis which were proved wrong.After Watson and Crick proposed the double helix model of DNA, three models for DNA replication were proposed: conservative, semiconservative and dispersive. But Meselson and Stahl proved semiconservative is actual the mode of DNA replication . So, dispersive and conservative replication are just hypothesis which were proved wrong.DNA replication has three possible methods: conservative, dispersive, and semi-conservative. Here, we focus on the Meselson-Stahl experiment, which proved DNA replication is semi-conservative. In this process, each new DNA pair consists of one old strand and one new strand, ensuring accurate genetic information transfer.
Compare conservative, semiconservative, and dispersive modes of DNA replication. Verified Solution This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
what is semi conservative dna replication
audemars piguet insolvent
Conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive DNA replication categories shaped scientists' research into how DNA replicated, which led to the conclusion that DNA replicated semi-conservatively. In 1956, Gunther Stent, a scientist at the University of California Berkeley in Berkeley, California, coined the terms conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive to .
DNA replication initiated from origins of replication proceeds in a semiconservative manner, such that each new copy of double-stranded DNA contains one original strand and one newly replicated .Semiconservative replication describes the mechanism of DNA replication in all known cells. . This process is known as semi-conservative replication because two copies of the original DNA molecule are produced, each copy conserving (replicating) the information from one half of the original DNA molecule. . Dispersive replication would .This suggested either a semi-conservative or dispersive mode of replication. The DNA harvested from cells grown for two generations in 14 N formed two bands: one DNA band was at the intermediate position between 15 N and 14 N, and the other corresponded to the band of 14 N DNA. These results could only be explained if DNA replicates in a semi .
celine ?anta fiyat
steps of semi conservative replication
Why Choose Cleveland Clinic Nevada. Request an Appointment. Providing Quality Healthcare Services in Nevada. Cleveland Clinic first began offering services in Las Vegas at Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health, which welcomed its .
conservative semiconservative and dispersive replication|semiconservative replication template