semiconservative dna replication means that Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The semiconservative model of DNA replication is shown. Gray indicates the original DNA strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized DNA. During DNA replication, each of the two strands that . You can create a logical volume (LV) by combining physical volumes into a volume group. LV provides more flexibility than using physical storage, and the created LVs can be extended or reduced without repartitioning or reformatting the physical device.
0 · why is dna replication semiconservative
1 · why dna is semiconservative
2 · what does semi conservative mean
3 · semiconservative replication refers to quizlet
4 · semiconservative nature of dna replication
5 · semi conservative meaning in biology
6 · rna polymerase is primarily responsible for
7 · explain the semi conservative mode
Our Protected Retirement Plan offers many features, including: Available as a standalone product, or as an investment option in a tax-efficient SIPP wrapper. Minimum investment of £10,000 – after any pension cash lump sum. Guaranteed income over a fixed term – of up to 25 years (minimum term applies). Flexi-access drawdown – clients can .
One of the most important concepts of DNA replication is that it is a semi-conservative process (Figure 7.2.7 7.2. 7). This means that every double helix in the new generation of an organism consists of one complete “old” .Semiconservative replication derives its name from the fact that this mechanism of transcription was one of three models originally proposed for DNA replication: • Semiconservative replication would produce two copies that each contained one of the original strands of DNA and one new strand. Semiconservative replication is beneficial to DNA repair. During replication, the new strand of D.
Learn how Meselson and Stahl tested the semiconservative replication model of DNA using isotopes and density gradient centrifugation. Find out how their experiment confirmed . DNA replication is a process that occurs during cellular division where two identical molecules of DNA are created from a single molecule of DNA. As a semiconservative process, . Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The semiconservative model of DNA replication is shown. Gray indicates the original DNA strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized DNA. During DNA replication, each of the two strands that .
One of the most important concepts of DNA replication is that it is a semi-conservative process (Figure 10.2.7 10.2. 7). This means that every double helix in the new . The Process of Semi-Conservative Replication. DNA replication occurs in preparation for mitosis, when a parent cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells – as each daughter cell contains the same .
Forming a new double strand from each strand of the original DNA molecule is called semiconservative replication. The term "semiconservative" captures the idea that each round .
By “semiconservative,” it is meant that the parental DNA subunits are conserved but that they become equally distributed into daughter molecules as replication proceeds. It was originally .Learn about semi-conservative replication of DNA on Khan Academy.According to the semiconservative replication model, which is illustrated in Figure 1, the two original DNA strands (i.e., the two complementary halves of the double helix) separate during .
DNA replication: The process by which DNA is copied in a cell. Semiconservative: Describes how newly formed double-stranded DNA molecules after replication contain one old strand and one new strand of .
During DNA replication, a double stranded DNA molecule separate, and each strand is used as a template for the synthesis of a new strand. This results in the formation of two identical copies of the original double stranded molecule. why is it called semi-conservative replication? The other template strand created during DNA replication is known as the lagging strand; On this strand, DNA polymerase moves away from the replication fork (from the 5’ end to the 3’ end) This means the DNA polymerase enzyme can only synthesise the lagging DNA strand in short segments (called Okazaki fragments) Explain the meaning of semiconservative DNA replication; Explain why DNA replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and lagging strand; Explain why Okazaki fragments are formed; Describe the process of DNA replication and the functions of the enzymes involved; Identify the differences between DNA replication in bacteria and eukaryotes In conservative replication, the parental DNA remains together, and the newly formed daughter strands are together. The semi-conservative method suggests that each of the two parental DNA strands act as a template for new DNA to be synthesized; after replication, each double-stranded DNA includes one parental or “old” strand and one “new .
The existence of cell division implies that there is a mechanism that replicates DNA and supplies identical copies for the daughter cells while still maintaining an accurate representation of the genome. This mechanism, known as DNA replication, occurs in all organisms and allows for genetic inheritance. It can occur in a short period, copying up to .
The semiconservative model of DNA replication is the correct model because each daughter DNA molecule consists of one parental strand and one new strand.The 2 DNA molecules created through replication, each contain one of the original strands paired with a newly synthesized strand. Because half of the original molecule is conserved in each molecule, replication is said to be semiconservative.Explain the meaning of semiconservative DNA replication; Explain why DNA replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and lagging strand; . This also means that it cannot add nucleotides if a free 3’-OH group is not available, which is the case for a single strand of DNA. The problem is solved with the help of an RNA sequence .
Figure 9.9 The semiconservative model of DNA replication is shown. Gray indicates the original DNA strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized DNA. . This means that approximately 1000 nucleotides are added per second. The process is much more rapid than in eukaryotes. Table 9.1 summarizes the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic .
After replication, each double-stranded DNA includes one parental or “old” strand and one “new” strand. This is known as semiconservative replication. The resulting DNA molecules have the same sequence and are divided equally into the two daughter cells. Replication in Prokaryotes. DNA replication uses a large number of proteins and .
The other template strand created during DNA replication is known as the lagging strand; On this strand, DNA polymerase moves away from the replication fork (from the 5’ end to the 3’ end) This means the DNA polymerase enzyme can only synthesise the lagging DNA strand in short segments (called Okazaki fragments) This mechanism of DNA replication is called semiconservative replication. This means that every double helix in the new generation of an organism consists of one complete “old” strand and one complete “new” strand wrapped around each other. . and the middle band faded. This was again consistent with the interpretation that DNA .DNA samples were then separated via centrifugation to determine the composition of DNA in the replicated molecules; The results after two divisions supported the semi-conservative model of DNA replication. After one division, DNA molecules were found to contain a mix of 15 N and 14 N, disproving the conservative mod el

The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site. . Finally, in 1958 Meselson and Stahl showed that the replication of DNA is indeed semiconservative with each daughter chromosome comprising an old, parental strand and a .As discussed in Chapter 3, DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. The central enzyme involved is DNA .Before a (parent) cell divides, it needs to copy the DNA contained within it. This is so that the two new (daughter) cells produced will both receive the full copies of the parental DNA; The DNA is copied via a process known as semi-conservative replication (semi = half). The process is called so because in each new DNA molecule produced, one of the polynucleotide DNA .
The Meselson-Stahl experiment demonstrated that DNA replication is semi-conservative, with each new DNA molecule containing one old strand and one new strand. The semiconservative DNA replication allows DNA repair mechanisms to work on the newly-synthesized DNA strand. Conclusion DNA replication is a semiconservative process as one of the two strands of the double-stranded DNA is an original DNA strand, which served as the template for the synthesis of the new strand. Semiconservative Replication. Definition. In this type of replication, one entirely old and entirely new DNA is produced. . Yes, DNA replication is semiconservative, with one parental and one newly synthesized strand. It is continuous on the leading strand but discontinuous, forming Okazaki fragments, on the lagging strand. .
why is dna replication semiconservative
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication was first demonstrated by the Meselson-Stahl experiment, which used isotopes of nitrogen to differentiate between old and new DNA strands. During semiconservative replication, each original strand of DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary new strand. . This means that after .
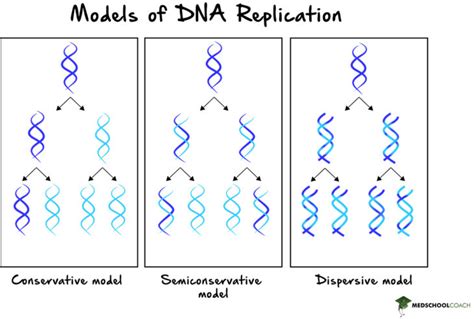
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication. In a round of replication, each of the two strands of DNA is used as a template for the formation of a complementary DNA strand. . The synthesis of the lagging strand by a discontinuous “backstitching” mechanism means that only the 5′-to-3′ type of DNA polymerase is needed for DNA . https://www.ibiology.org/genetics-and-gene-regulation/semi-conservative-replication-of-dna/About this talk: In 1958, Matthew Meselson and Frank Stahl publish.As Fig. 8.1 shows, there are several ways in which one could imagine going from one double helix (duplex) to two. In conservative replication (Fig. 8.1A), some mechanism copies both strands to make an all-new double-strand molecule. Semiconservative replication (Fig. 8.1B) requires splitting the original duplex and forming a complimentary copy of each strand.
Meselson and Stahl experiment gave the experimental evidence of DNA replication to be semi-conservative type.It was introduced by the Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in the year 1958.Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl have used E.coli as the “Model organism” to explain the semiconservative mode of replication. There are three modes of replication introduced .
Learn about semi-conservative replication of DNA on Khan Academy.
hermes passport holder inside
rolex купити
Vakances. 2011-01-01. Pašlaik CERT.LV nav aktuālas vakances. Tomēr vienmēr esam gatavi apsvērt sadarbību ar kiberdrošībā zinošiem un motivētiem cilvēkiem. Ja jums ir interese par darbu kiberdrošības jomā, rakstiet uz [email protected].
semiconservative dna replication means that|rna polymerase is primarily responsible for